How to Design A Hydraulic Cylinder?
Hydraulic cylinder is a kind of complicated device containing a great deal of components in the environment of industrial manufacturing. Many factors are to be considered in the process of designing a hydraulic cylinder. None of these factors should be ignored because it will cause the design mistakes. Different working conditions of hydraulic cylinders affects the design standards. For instance, hydraulic cylinders used in construction industry versus agricultural industry require other design material. The following are some factors that should be considered in the process of designing a hydraulic cylinder.
The design process begins by thoroughly understanding the application for which the cylinder will be used.
Key parameters include:
• The force required
• Stroke length
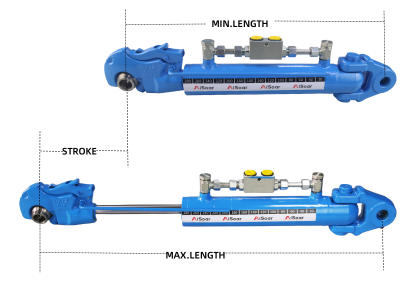
• Operating pressure
• Mounting style (e.g., flange, clevis, trunnion)
There are several advantages and limitations of each mounting style. When customizing a hydraulic cylinder, you need to choose an appropriate mounting style according to your application. In Aisoar Hydraulics, there are seven mounting options of customized welded hydraulic cylinders: clevis, cross-tube, flange, tang, trunnion, spherical bushings and foot mount. As for customized tie rod hydraulic cylinders, mounting options are tie-rod extended, flange, trunnion, fixed eye clevis and foot mount
• Rod diameter
• Environment (e.g., temperature, potential contaminants)
Working conditions are the important factors: where the hydraulic cylinder is designed to do and what kind of working capacity it needs to bear. If the hydraulic cylinder is used in underwater conditions, technicians should consider how to prevent the water from flowing into hydraulic oil. The marine environment requires hydraulic cylinder with high corrosion resistance. Similarly, if the hydraulic cylinder is working in the construction equipment, it should withstand extreme load and temperatures.
Step 2: Choose a Cylinder Type
Decide whether a single or double acting cylinder is needed based on whether the application requires power in one direction or both.
Step 3: Calculate Size and Specifications
Based on the force needed and the available operating pressure, calculate the bore size. Ensure the rod diameter is sufficient to prevent buckling and meets any mounting or load requirements.
Step 4: Select Material and Coatings
Choose materials for the cylinder body and rod that provide the necessary strength and corrosion resistance. Coatings may be needed for additional protection, depending on environmental exposures.
Step 5: Design the Seals and Bearings
Select seals that can handle the system’s pressure and any thermal or chemical concerns. Similarly, choose bearings that can withstand the load and any alignment issues.
Step 6: Design for Manufacturability
Ensure that the design is feasible for manufacturing, considering available machining techniques, cost-effectiveness, and assembly processes.
Step 7: Create Detailed Engineering Drawings
Produce detailed drawings specifying all dimensions, tolerances, and material specifications.
Step 8: Prototype and Test
Before full production, build a prototype for inspecting and testing. Subject the prototype to operating pressures, loads, and cycles to ensure it meets all performance criteria.
Step 9: Analyze and Refine
After testing, analyze the results and refine the design as needed to enhance performance or address any issues.


AISOAR HYDRAULIC CYLINDERS
Hengxin Mansion, No. 588, Jiangnan Main Road, Changhe Street, Binjiang District, Hangzhou City, Zhejiang Province, China
TEL: +86-571-87920309
Contact name: Tracy
Mobilephone: +8618248492500
Wechat: aisoar03
EMAIL: tracy@ai-soar.com


 ES
ES RU
RU