How Does a Hydraulic Cylinder Work?
Are you tired of struggling with inefficient machinery? A faulty hydraulic cylinder could lead to costly downtime and delays. The solution? High-quality hydraulic cylinders that ensure efficiency, reliability, and seamless performance in your operations.
A hydraulic cylinder is a mechanical actuator that converts hydraulic energy into linear force and motion. It works by applying fluid pressure to a piston, which moves to perform tasks like lifting, pushing, or pulling.
Keep reading to explore the basics of hydraulic cylinders, their types, and how to choose the right one for your needs.
What is a Hydraulic Cylinder?
Principle of the Hydraulic Cylinder
A hydraulic cylinder is a critical component in hydraulic systems used to produce linear force and motion. It consists of a cylindrical barrel, a piston, and a piston rod. Pressurized hydraulic fluid pushes against the piston, causing the piston rod to extend or retract. This simple yet powerful mechanism is widely used in heavy machinery, industrial equipment, and agricultural tools.
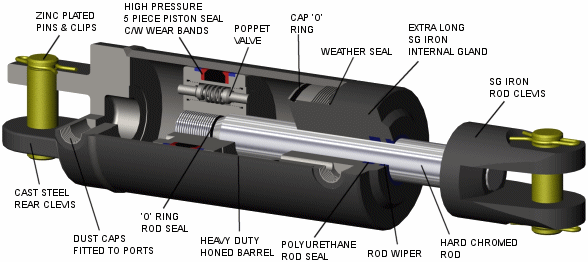
Components of Hydraulic Cylinder
| Cylinder Part | Description | Common Materials |
| Cylinder Barrel | Main body that houses the piston and fluid. | Steel (Seamless or Honed Tubes), Cast Iron |
| Piston | Divides the cylinder and moves under pressure. | Steel, Cast Iron, Aluminum |
| Piston Rod | Transfers force from the piston to the load. | Chrome-Plated Steel, Stainless Steel |
| End Caps (Cylinder Heads) | Seals the ends of the cylinder. | Cast Iron, Steel, Aluminum |
| Rod Gland | Prevents fluid leakage at the rod opening. | Steel, Aluminum, Brass |
| Seals and O-Rings | Prevent leaks and maintain pressure. | Nitrile Rubber (NBR), Polyurethane, Fluorocarbon (Viton) |
| Bearings | Support the piston rod and reduce friction. | Bronze, Composite Materials, Nylon |
| Hydraulic Fluid | Transfers energy and lubricates components. | Hydraulic Oil (Mineral or Synthetic) |
| Hydraulic Port | Entry/exit point for fluid. | Steel or Stainless Steel Fittings |
| Cushioning Device | Reduces impact at the end of the piston stroke. | Steel, Bronze |
How Hydraulic Cylinders Work?
To understand how hydraulics work, imagine a syringe. When you push the plunger, the liquid inside generates pressure that forces it out. Similarly, in a hydraulic system, a pump forces pressurized hydraulic fluid into the cylinder, creating energy to move the piston.
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how hydraulic cylinders work:
1.Hydraulic Fluid Entry: A pump directs pressurized hydraulic oil into the cylinder.
2.Piston Movement: The pressurized fluid acts on the piston, moving it in the desired direction (extend or retract).
3.Linear Force Generation: The movement of the piston creates linear motion and force to perform work like lifting or pushing.
4.Fluid Return: The fluid exits through a return line, completing the cycle.
Hydraulic cylinders rely on high-quality seals and precision engineering to prevent leaks and maximize efficiency, ensuring smooth performance in even the most demanding environments.
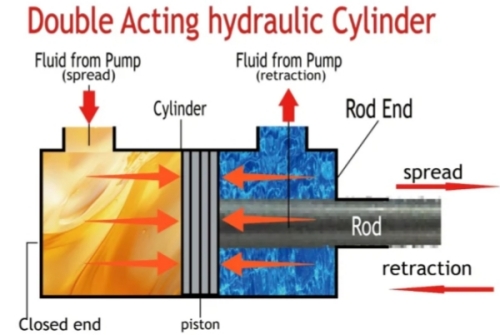
Double Acting Hydraulic Cylinder :
Step 1: Extension Stroke
When hydraulic fluid is applied to the cylinder's base, it forces the piston and rod to move outward. The hydraulic pressure pushes the piston up the bore, extending the rod for tasks requiring a pushing force.
Step 2: Retraction Stroke
When the fluid flow is reversed, it enters the rod end, moving the piston back towards the base. The fluid in the cap end is expelled, and the rod retracts, providing a pulling force, controlled in speed and pressure like the extension stroke.
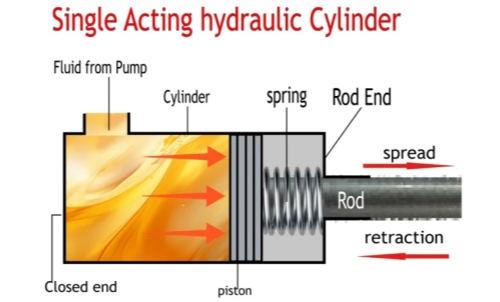
Single Acting Hydraulic Cylinder:
Step 1: Hydraulic Pressure for Extension
In a single-acting cylinder, hydraulic fluid enters through one port, applying pressure to the piston. This pressure forces the piston to move, extending the piston rod to lift a load or push an object.
Step 2: Retraction Mechanism
Unlike double-acting cylinders, a single-acting cylinder uses an external force, usually a spring, for retraction. When hydraulic pressure is released, the spring decompresses, pulling the piston back. In some cases, the weight of the load also helps retract the rod.
Types of Hydraulic Cylinders
Hydraulic cylinders come in various designs, tailored for different applications. Here are the most common types:
Tie-Rod Cylinders: These are lightweight cylinders with tie rods holding the cylinder’s components together. They’re ideal for industrial applications where compact size is critical.
Welded Cylinders: Built for durability, welded cylinders feature a strong, enclosed design suitable for heavy-duty applications like construction machinery.
- Double-Acting Cylinders: These cylinders exert force in both extending and retracting motions, offering precise control and versatility.
- Single-Acting Cylinders: These exert force in one direction only, often relying on gravity or an external force for retraction.
Telescopic Cylinders: These multi-stage cylinders are designed to provide long strokes in compact spaces, often used in dump trucks and cranes.
Each type of hydraulic cylinder has its strengths, making it important to choose the right one based on your specific needs

How to Choose a Hydraulic Actuator?
Choosing the right hydraulic cylinder can significantly impact the performance and reliability of your machinery. Here’s what to consider:
| Selection Factor | Description | Key Considerations |
| Load Requirements | The amount of force the actuator needs to generate. | Match cylinder force with load needs. |
| Stroke Length | The distance the piston rod needs to extend or retract. | Ensure sufficient piston movement. |
| Operating Pressure | The hydraulic pressure the actuator must handle. | Match the cylinder’s pressure rating with your hydraulic system (e.g., 1500 PSI, 3000 PSI). |
| Cylinder Type | The specific design suited for the application. | Choose based on application (e.g., tie-rod, welded). |
| Application Environment | Conditions where the cylinder will operate. | Consider temperature, humidity, exposure to dirt, dust, water, or chemicals. |
| Mounting Style | How the cylinder will be mounted to the machine. | Select from clevis, flange, trunnion, or other mounting styles |
| Seal Material | The material used for seals to prevent fluid leaks. | Choose seal materials (e.g., NBR, Viton, Polyurethane) based on operating temperature, pressure. |
| Space Constraints | Available space for cylinder installation. | Consider compact cylinders (e.g., telescopic) if installation space is limited. |
What Are Hydraulic Cylinders Used For?
Hydraulic cylinders are versatile components used in a wide range of applications:
1.Agriculture: Powering machinery like tractors, plows, and harvesters for heavy lifting and pulling tasks.
2.Construction: Enabling movement in excavators, loaders, bulldozers, and cranes to handle earthmoving and heavy loads.
3.Manufacturing: Automating processes like stamping, pressing, and molding for increased productivity.
4.Automotive: Supporting car lifts, dump trucks, and specialized vehicles in lifting and tipping operations.
5.Marine: Assisting in ship deck machinery, steering systems, and offshore equipment.


Their ability to deliver immense force with precision makes hydraulic cylinders indispensable across industries.

AISOAR HYDRAULIC CYLINDERS
Hengxin Mansion, No. 588, Jiangnan Main Road, Changhe Street, Binjiang District, Hangzhou City, Zhejiang Province, China
TEL: +86-571-87920309
Email: sales@ai-soar.com
Website: www.aisoarhydraulics.com


 ES
ES RU
RU