How does a double-acting hydraulic cylinder work?
CONTENT
1. Article Introduction
2. What Is a Double Acting Hydraulic Cylinder?
3. How Does a Double Acting Hydraulic Cylinder Work?
4. Advantages of Double Acting Hydraulic Cylinders Over Single Acting Cylinders
5. Applications of Double Acting Hydraulic Cylinders
6. How to Properly Size and Select a Double Acting Hydraulic Cylinder for Your Application
7. Conclusion
Are you struggling with inefficient machinery or inconsistent movements in your hydraulic systems? This can lead to poor performance, costly downtime, and increased repair expenses. The solution? Understanding how a double acting hydraulic cylinder works to provide reliable, controlled motion for your equipment. Read on to learn how these cylinders enhance productivity and efficiency.
A double-acting hydraulic cylinder uses hydraulic pressure to move the piston in both directions, generating force for extension and retraction, with fluid entering different chambers on either side of the piston to control movement.
Want to optimize your machinery's performance? Let’s dive into how double-acting hydraulic cylinders work and why they’re crucial for heavy-duty equipment in industries like construction, agriculture, and manufacturing.
What is a Double Acting Hydraulic Cylinder?
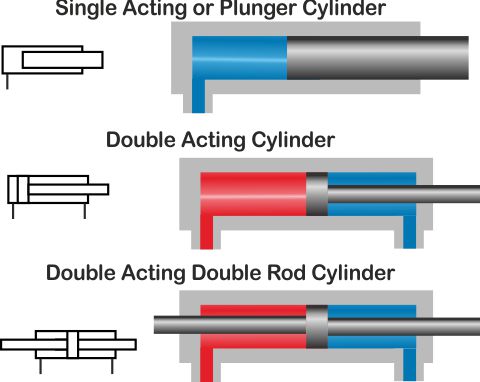
A double-acting hydraulic cylinder is a type of actuator commonly used in hydraulic systems to create linear motion in both directions. Unlike single-acting cylinders, which generate force in only one direction, a double-acting cylinder uses hydraulic pressure to move the piston both forward and backward, enabling it to extend and retract. This bi-directional functionality makes it versatile and efficient for a wide range of industrial applications.
The cylinder consists of a cylindrical barrel, a piston that moves inside the barrel, and a piston rod that extends from one end of the cylinder. The barrel is divided into two chambers by the piston: one for the rod side (extension) and one for the cap side (retraction). Hydraulic fluid is pumped into these chambers to push the piston in the desired direction, generating the force needed to power mechanical systems. The force during extension is slightly greater than during retraction because of the differing effective areas exposed to hydraulic fluid. To handle varying environments, the diameter of the piston rod can be adapted, with robust designs preventing bending under load in both horizontal and vertical orientations. The rod is typically chrome-plated or surface-hardened for durability and a finely finished surface, ensuring reliable sealing over extended use.
Accurate machining of all components guarantees smooth, efficient motion, making double-acting cylinders the most commonly used type in hydraulic systems, capable of providing powerful and reliable output strokes in two directions.
Double-acting cylinders are commonly used in machinery where movement in both directions is needed to complete tasks such as lifting, pushing, or pulling. Their ability to apply force in both directions makes them ideal for heavy-duty and high-force applications.
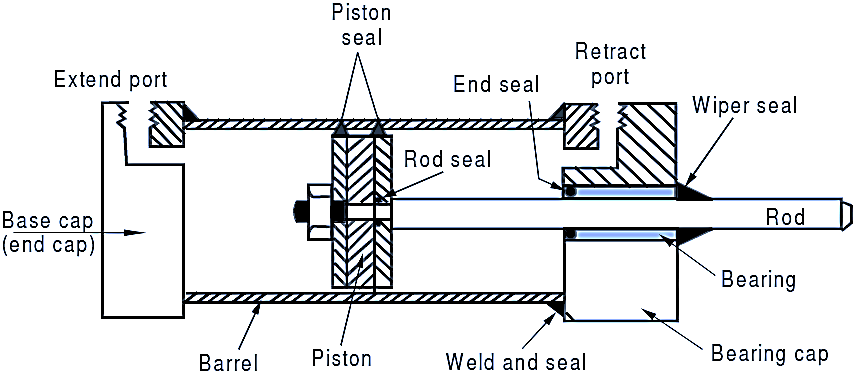
How Does a Double Acting Hydraulic Cylinder Work?
 When the piston rod flexes and stretches, a double-acting cylinder will force or move the liquid from either end of the piston. The seal between the outer diameter of the piston and the inner diameter of the cylinder must be able to deal with both direction and movement issues. Furthermore, it could also be a dual-sided rod cylinder, which incorporates a piston rod extension motion via the cylinder's back cover.
When the piston rod flexes and stretches, a double-acting cylinder will force or move the liquid from either end of the piston. The seal between the outer diameter of the piston and the inner diameter of the cylinder must be able to deal with both direction and movement issues. Furthermore, it could also be a dual-sided rod cylinder, which incorporates a piston rod extension motion via the cylinder's back cover.
The operation of a double acting hydraulic cylinder involves the use of hydraulic fluid to create pressure, which powers the movement of the piston inside the cylinder. When the hydraulic fluid is pumped into one of the chambers of the cylinder, it creates a force that moves the piston in one direction—either extending the piston rod or retracting it, depending on the side where the fluid is applied.
In more detail, when fluid enters the cap side of the cylinder, it pushes the piston and rod out, extending the piston rod. Conversely, when fluid enters the rod side, it pushes the piston in the opposite direction, causing the rod to retract. The controlled movement of fluid in both directions ensures that the cylinder operates smoothly and efficiently.
This bi-directional motion is essential for a wide range of applications, as it allows the cylinder to perform tasks such as lifting, pushing, or pulling in both directions. The precise control over the fluid pressure also allows for accurate movements, making double-acting hydraulic cylinders ideal for tasks requiring high precision and power.
Advantages of Double Acting Hydraulic Cylinders Over Single Acting Cylinders
While both double acting hydraulic cylinders and single-acting cylinders use hydraulic pressure to generate movement, double-acting cylinders offer several key advantages:
| SINGLE-ACTING | DOUBLE-ACTING | |
| Retraction Method | Return spring, load,or gravity | Hydraulic return |
| Connection Ports | 1 | 2 |
| Advantages | ✔ Simlicity ✔ Requires just 1 hose percylinder ✔ Economical ✔ Easy to maintain | ✔ Precise control ✔ Faster retraction ✔ Suits repetitive actions ✔ Applies push and pull forces |
| Disadvantage | ✖ Pushes in just one direction. ✖ Less controlled retraction. ✖ Springs can wear out. | ✖ More complex ✖ Needs 2 x hoses ✖ Cost ✖ Requires pump with a 4-way valve |
| Useful for | 1) Simple lifting jobs. 2) Light industrial and commercial applications 3) When fast retraction is notessential | 1) Repetitive actions. e.g. jack and crib applications. 2) Presses, or when the cylinder is upside down. 3) When you want both pushing and pulling forces 4) When very long hoses are required. 5) A controlled retraction time. |
Overall, double-acting hydraulic cylinders provide superior performance, efficiency, and control over their single-acting counterparts, making them the preferred choice for many industrial applications.
Applications of Double Acting Hydraulic Cylinders
Double acting hydraulic cylinders are widely used across various industries, primarily because of their ability to generate force in both directions. Some of the most common applications include:
| APPLICATION | |
| Construction and Heavy Equipment | Cranes ,Excavators ,Backhoes ,Bulldozers, Loaders |
| Agricultural Machinery | Tractors, Sprayers,Plows,Harvesters |
| Industrial Automation | Robotics,Press Machines,Material Handling Systems |
| Marine Applications | Ship Steering Systems,Winches and Cranes,Hatch Covers |
| Aerospace and Defense | Car Lifts , Hoists,Dump Trucks |
How to Properly Size and Select a Double Acting Hydraulic Cylinder for Your Application
1. Understand the Application Requirements
- Load: Determine the force required to move the load in both extension and retraction.
- Stroke Length: Measure the total distance the cylinder needs to extend and retract.
- Speed: Define the desired speed for extension and retraction.
- Orientation: Consider the mounting position and alignment with the load (horizontal, vertical, or angled).
- Cycle Frequency: Estimate the number of cycles per minute, hour, or day to determine wear and heat dissipation needs.
2. Determine the Force Requirements
Use the formula to calculate the required force:
F=P×A
Where:
F: Force (lbs or N)
P: Hydraulic pressure (psi or bar)
A: Effective piston area (square inches or square centimeters)
For extension force: Use the piston area.
For retraction force: Use the area of the piston minus the area of the rod.
Example:
If you need 10,000 lbs of force and your system operates at 2,500 psi:
A=P/ F=10,000/2500 =4 in²
Choose a cylinder with a piston that provides at least this area.
3. Select the Appropriate Cylinder Bore
- The bore diameter determines the cylinder’s force output.
- Larger bore sizes produce more force but require higher fluid volumes.
- Confirm the bore size aligns with your calculated force needs.
4. Choose the Rod Diameter
- The rod diameter affects the retraction force, buckling strength, and rigidity.
- For heavy loads or long strokes, select a thicker rod to prevent bending or buckling.
5. Define the Stroke Length
- Ensure the stroke length accommodates the full range of motion needed.
- Consider the retracted length of the cylinder to ensure it fits within the available space.
6. Pressure Rating
- Verify the cylinder’s pressure rating matches or exceeds your system’s maximum operating pressure.
- Factor in a safety margin, typically 1.5 to 2 times the operating pressure.
7. Mounting Style
- Select a mounting configuration that suits your application:
- Flange Mounts: Ideal for fixed applications.
- Clevis or Trunnion Mounts: Suitable for pivoting applications.
- Foot Mounts: Common in stationary setups.
8. Consider Environmental Factors
- Temperature: Ensure seals and materials can handle the operating temperature range.
- Corrosion Resistance: For outdoor or marine environments, choose corrosion-resistant coatings or materials (e.g., stainless steel).
- Contamination: Install protective bellows or covers in dusty or dirty environments.
9. Hydraulic Flow and Speed
- Determine the flow rate of your hydraulic system to ensure it matches the desired cylinder speed.
- Use the formula to estimate speed:
V=Q/A
Where:
- V: Velocity
- Q: Flow rate (gallons per minute or liters per minute)
- A: Piston area
By carefully analyzing these factors and working with a reputable supplier, you can select a double-acting hydraulic cylinder tailored to your specific application.
By understanding how these cylinders operate and choosing the right one for your application, you can harness their full potential to improve efficiency, reduce downtime, and meet the demands of even the most challenging environments. From construction sites to factory floors, the double-acting hydraulic cylinder remains an indispensable tool driving productivity and innovation.

AISOAR HYDRAULIC CYLINDERS
Hengxin Mansion, No. 588, Jiangnan Main Road, Changhe Street, Binjiang District, Hangzhou City, Zhejiang Province, China
TEL: +86-571-87920309
Email: sales@ai-soar.com
Website: https://www.aisoarhydraulics.com/


 ES
ES RU
RU